CO-PRODUCTS
Optimal recovery of the raw materials used
The ethanol production processes generate various co-products that are used in animal feed, agriculture, and industry.
These co-products contribute to the optimal recovery of the raw materials used, supporting a circular economy.
There are three categories of co-products generated by ethanol production:
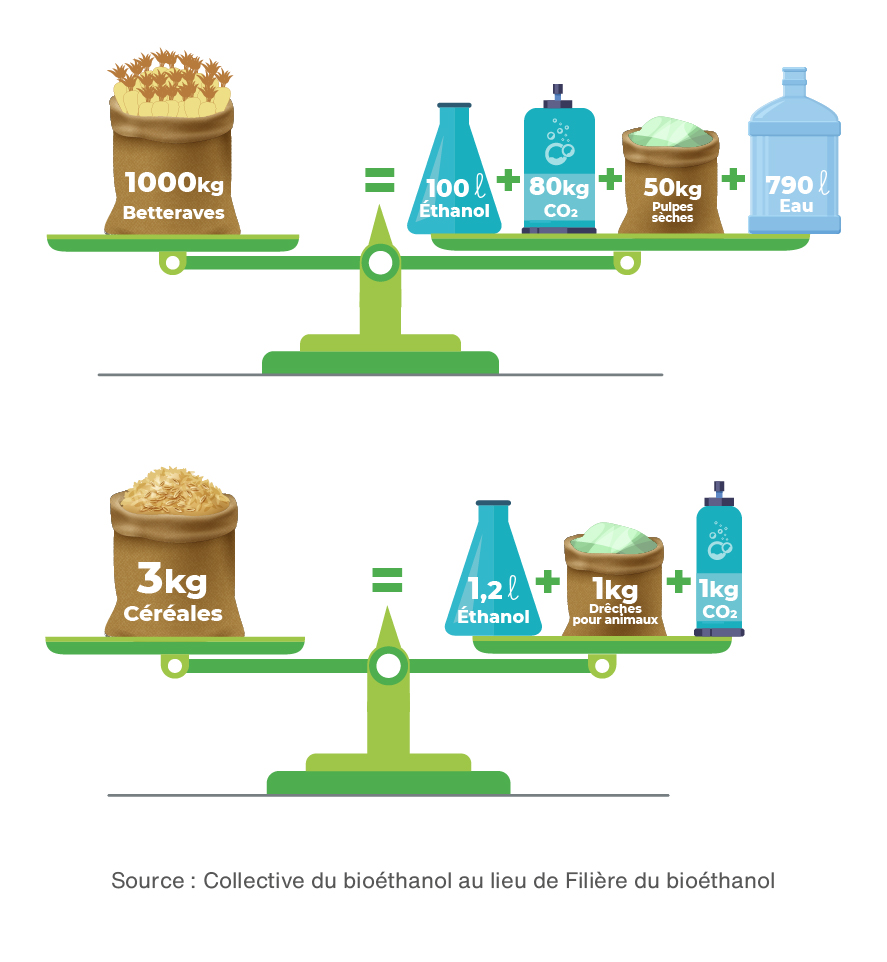
1 – Co-products resulting from the processing of sugar beets
2 – Co-products resulting from the processing of cereals
3 – Carbon dioxide (CO₂), common to all raw materials
1) Co-products resulting from the processing of sugar beets
During ethanol production from sugar beets, two main co-products are generated: beet pulp and vinasse.
Beet pulp
The pulp results from the crushing of sugar beets and is rich in fiber. They can be used in animal feed after being pressed or dehydrated.
Vinasses
Vinasse is the product that remains after the sugar beet has been processed into sugar. It is a natural and powerful fertilizer, particularly rich in potash.
2) Co-products resulting from the processing of cereals
In the process of converting cereals into alcohol, distillers’ grains constitute the main co-product.
Wheat and corn distillers’ grains
The distillers’ grains resulting from cereal processing are rich in protein, making them a high-nutritional-value feed for animals.
They promote the development of muscle rather than fat, since the sugars and starches have been converted into alcohol.
3) Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Carbon dioxide is generated during the fermentation process at a rate of one ton of CO₂ for one ton of alcohol.
Once recovered and purified, it can be used in various applications, such as in greenhouses to promote plant growth, or in the food industry for carbonated beverages, for example.
Carbon dioxide can also be used for the production of synthetic fuels (including sustainable aviation fuels), in combination with hydrogen obtained through water electrolysis.