THE MAINOUTLETS
Applications across many sectors
Ethyl alcohol, Ethyl alcohol, also known as ethanol, is a molecule with multiple uses and plays a central role in many sectors of activity.
Ethyl alcohol, derived from the fermentation of sugars and starch contained in agricultural raw materials (such as sugar beet, sugarcane, or cereals), is used both in industrial applications and in everyday life.
Two main markets for ethanol use can be distinguished:
The traditional alcohol marke, The traditional alcohol market, which includes uses in the food industry (notably spirits), cosmetics, perfumery, pharmaceuticals, the chemical industry, and disinfection (such as hydroalcoholic gels).
The rapidly growing bioethanol fuel market, which corresponds to the use of ethanol in fuels or in a derived form (ETBE) for gasoline engines.
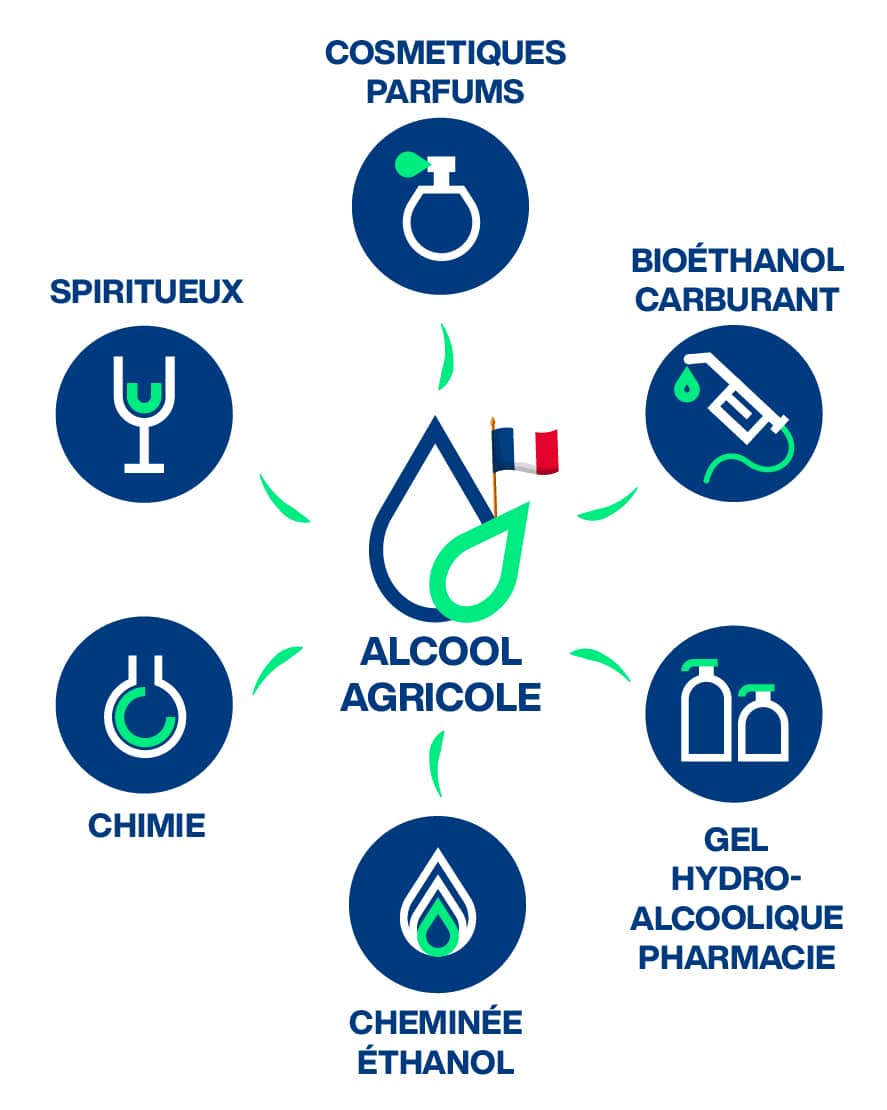
1) Traditional alcohol
Traditional alcohol is used across various industries for its specific properties:
- Alcoholic beverages:: the main ingredient in spirits.
- Food industry : used as a preservative or additive, or to produce vinegar.
- Pharmacy : used as an excipient and solvent in the manufacture of medicines, or for the production of hydroalcoholic gels.
- Cosmetics and perfumery : used in perfumes, lotions, and other personal care products.
- Parachemicals and industry : used as a solvent or cleaning agent in many industrial processes, and as a raw material for the production of certain molecules (such as ethyl acetate).
2) Bioethanol fuel
Bioethanol fuel is a renewable biofuel. It is used, just like its derivative ETBE, as a component in gasoline to increase the octane rating (historically replacing lead), reduce CO₂ emissions, and promote more sustainable mobility. It is found in gasoline-type fuels such as SP95, SP98, SP95-E10, and Superethanol-E85.
